Cybersecurity threats are an ongoing concern for businesses and organizations of all sizes. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other malicious activities can cause significant financial losses, reputational damage, and disruptions to critical operations. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) offers a valuable tool to help organizations manage and reduce these risks. This framework provides a standardized approach to identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents, as well as providing an overall governance framework.
What is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a set of guidelines based on existing standards and best practices. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, but rather a flexible framework that allows organizations to tailor their cybersecurity efforts to their specific needs and risk profile.
The current version, NIST CSF 2.0, was published in February 2024. It expands on the original framework by incorporating a wider range of considerations, including supply chain security and privacy.
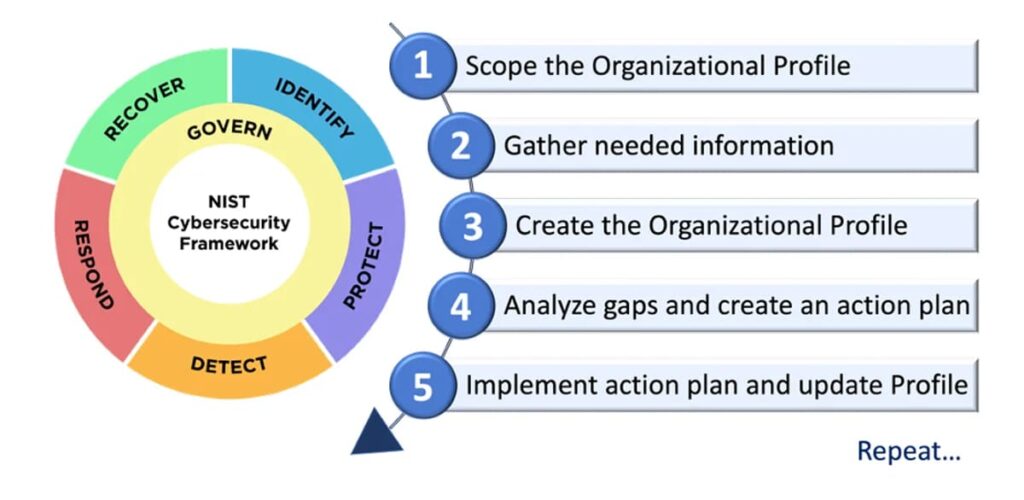
The Core of the NIST CSF: Governance, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is built on six core functions:
- Governance: The organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy are established, communicated, and monitored.
- Identify: This function involves understanding your organization’s assets, data, and systems, along with the potential threats and vulnerabilities they face.
- Protect: Here, the focus is on implementing safeguards to protect your assets from cyberattacks. This includes measures like access controls, firewalls, and data encryption.
- Detect: Early detection of a cybersecurity incident is crucial. This function involves having systems in place to continuously monitor your network and systems for suspicious activity.
- Respond: When a security incident occurs, a well-defined response plan is essential. This function helps organizations contain the damage, identify the root cause, and take steps to prevent similar incidents in the future.
- Recover: The goal of this function is to restore normal operations and functionality as quickly as possible after a cyberattack. This includes having backups of critical data and systems.
Cybersecurity Framework Governance Function
Governance is one of the core functions of the framework, the following are some of the benefits of having a strong governance process in place.
- Aligns cybersecurity with business objectives
Governance ensures that cybersecurity strategies and initiatives are aligned with the overall business goals and risk appetite.
This prevents security efforts from becoming isolated and ensures that they contribute to the organization’s success.
- Establishes clear accountability
Governance defines roles, responsibilities, and authorities for cybersecurity activities, ensuring that everyone knows who is accountable for what.
This reduces confusion and increases efficiency.
- Provides oversight and assurance
Governance provides a mechanism for oversight and assurance, allowing senior management to monitor cybersecurity performance and ensure that risks are being managed effectively. - Enhances risk management
Governance helps organizations to identify, assess, and manage cybersecurity risks in a structured and systematic way.
This reduces the likelihood of security incidents and minimizes their impact when they do occur.
- Facilitates compliance
Governance can help organizations to comply with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. This reduces the risk of fines and penalties and protects the organization’s reputation. - Improves decision-making
Governance provides a framework for making informed decisions about cybersecurity investments and initiatives.
This ensures that resources are allocated effectively and that the organization is prepared to respond to emerging threats.
- Creates a culture of security
Governance can help to create a culture of security within the organization, where everyone is aware of their role in protecting the organization’s assets.
This makes the organization more resilient to cyberattacks.
The NIST CSF 2.0 specifically emphasizes the importance of governance by making it one of its core functions.
The framework provides guidance on how to establish a governance structure, define roles and responsibilities, and implement oversight and assurance mechanisms.
By providing a framework for aligning cybersecurity with business objectives, establishing accountability, managing risks, and facilitating compliance, governance can help organizations to protect their assets and reduce their exposure to cyber threats.
About Control Sets
In the context of a cybersecurity framework, there’s no single “best” control set for every organization. The most suitable set depends on several factors specific to your organization. Here’s why:
- Risk Profile: Different organizations face different cybersecurity risks. A small business with limited online presence might prioritize controls around data encryption and user access management, while a large healthcare provider might focus more on controls for protecting sensitive patient data and detecting malware.
- Industry Regulations: Some industries have specific compliance requirements related to cybersecurity. For example, a financial institution might need to implement controls aligned with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework Supplement for Business: Financial Services Sector.
- Organizational Resources: Implementing security controls requires resources like budget, manpower, and expertise. Smaller organizations might need to prioritize a core set of essential controls before expanding to more advanced measures.
Here are some control sets to consider:
- NIST Special Publication 800-53, Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations, is a set of recommended security and privacy controls for federal information systems and organizations to help meet the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) requirements.
- ISO 2700 is an international standard that provides a framework for organizations to establish, implement, operate, monitor, review, maintain, and continually improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology) is a globally recognized set of controls that helps organizations optimize their governance of information and technology. It provides a comprehensive set of controls and practices to ensure that IT aligns with business objectives, reduces risk, and improves efficiency.
- CIS Critical Security Controls: This set of 20 critical security controls is a good starting point for smaller organizations or those with limited resources.
- Industry-Specific Control Sets: Control Sets like HIPAA for healthcare or NERC-CIP for critical infrastructure provide tailored controls relevant to specific industry risks.
Here’s a recommended process to find the best control set:
- Identify Your Risk Profile: Assess your organization’s assets, data, and potential threats.
- Review Industry Regulations: Check if your industry has specific compliance requirements.
- Consider Resources: Evaluate your budget, manpower, and expertise for implementing controls.
- Choose a Control Set: Select a control set that aligns with your risk profile, industry, and resources.
Remember, the best control set is one that is implemented effectively. Regular testing and updates are crucial for maintaining strong cybersecurity.
Conclusion
By adopting the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and a suitable control set, organizations can significantly strengthen their cybersecurity posture, protect critical assets, and build resilience against cyber threats.
Contact us to find out how we can help you with the implementation of a cybersecurity framework to protect your business and its assets.